Buy azithromycin online offers a convenient way to obtain this commonly prescribed antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections such as respiratory infections, skin conditions, and sexually transmitted diseases. Ensure you purchase from a reputable source with a valid prescription to guarantee safe and effective treatment.
Prevention Strategies
-
Improved Sanitation and Hygiene: Access to clean water, proper waste management, and handwashing.
-
Vector Control: Eliminate breeding sites for mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects.
-
Safe Food Handling: Cook food thoroughly, avoid undercooked meat, and wash fruits and vegetables.
-
Protective Measures: Wear insect repellent, and protective clothing, and use bed nets.
Buy mebendazole from Dosepharmacy allows you to easily access this anti-parasitic medication, commonly used to treat intestinal worm infections like pinworms, roundworms, and hookworms. Always follow the prescribed dosage and guidelines provided by your healthcare professional for safe and effective use of the medication.
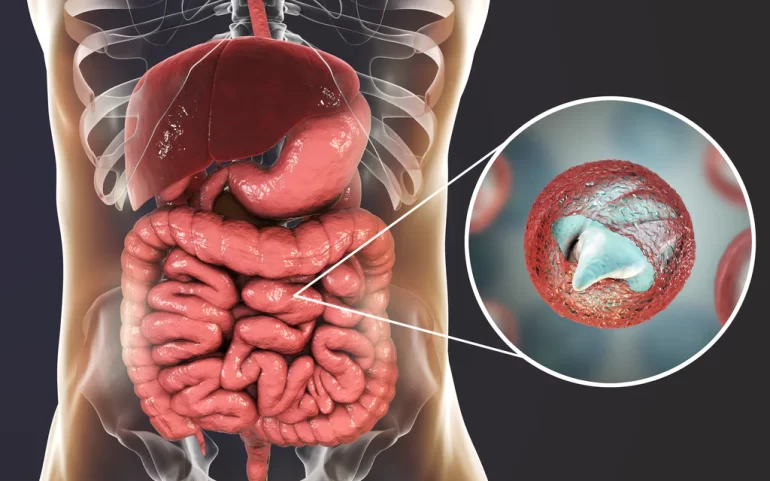
1. Recognizing the Symptoms of Parasitic Infections
The first step in fighting parasitic infections is recognizing the symptoms, which vary depending on the type of parasite involved. Common symptoms of parasitic infections include:
- Digestive Issues: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea are common signs of intestinal parasites such as Giardia or tapeworms.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Parasitic infections can cause fatigue, weakness, and anemia due to nutrient depletion.
- Skin Rashes or Itching: Some parasites, like scabies or lice, cause itching, skin irritation, and visible sores.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can occur if the parasite consumes nutrients from the host.
- Fever and Chills: Some parasitic infections, such as malaria, present flu-like symptoms including fever, chills, and muscle aches.
2. Consulting a Doctor for Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect a parasitic infection, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Proper diagnosis is critical, as the symptoms of parasitic infections can be similar to other illnesses. Your doctor may conduct stool tests, blood tests, or imaging studies to identify the parasite.
Once diagnosed, your doctor will prescribe a specific treatment plan, which may include:
- Antiparasitic Medications: Drugs such as mebendazole, albendazole, or ivermectin are commonly prescribed to kill parasites. The medication will depend on the type of parasite and its severity.
- Antibiotics: In cases where a secondary bacterial infection occurs, antibiotics may be prescribed in conjunction with antiparasitic medication.
- Rehydration Therapy: If the infection causes severe diarrhea or vomiting, rehydration therapy may be needed to restore lost fluids and electrolytes.
3. Preventing Parasitic Infections
Prevention is a critical component in the fight against parasitic infections. By adopting a few basic practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
- Hygiene Practices: Regular hand washing with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the restroom, can help prevent the spread of parasites.
- Food and Water Safety: Avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat and seafood. Ensure fruits and vegetables are washed thoroughly, and drink only clean, safe water. In areas where water contamination is a concern, boil water or use a reliable filter before drinking.
- Proper Sanitation: In areas with inadequate sanitation, proper disposal of human and animal waste is essential to prevent parasite transmission.
- Avoid Contaminated Soil and Water: Parasites such as hookworms can be transmitted through contaminated soil. Wear protective footwear when walking in potentially contaminated areas.
Diagnosis and Treatment
-
Accurate Testing: Laboratory tests, imaging studies, and physical examinations.
-
Antiparasitic Medications: Ivermectin, Albendazole, and Metronidazole.
-
Supportive Care: Rest, hydration, and nutrition.
Awareness and Education
-
Public Health Campaigns: Educate communities on prevention and symptoms.
-
Healthcare Provider Training: Enhance diagnosis and treatment capabilities.
-
Community Engagement: Encourage participation in prevention efforts.
Integrating Traditional and Modern Medicine
-
Herbal Remedies: Explore the efficacy and safety of traditional treatments.
-
Synthetic Medications: Develop and distribute effective antiparasitic drugs.
Research and Development
-
Vaccine Development: Investigate vaccines for parasitic infections.
-
Novel Therapies: Explore new treatments and drug combinations.
-
Epidemiological Studies: Monitor and analyze infection patterns.
Global Collaboration
-
International Partnerships: Share knowledge, resources, and expertise.
-
Funding and Support: Allocate resources for research and program implementation.
-
Policy Development: Establish guidelines and standards for parasite control.
Conclusion
FAQs
A: Malaria, toxoplasmosis, hookworm, and scabies.
A: Practice good hygiene, use protective measures, and ensure safe food handling.