Popular and quite successful for shrinking stomach size to cure obesity is gastric bypass surgery, sometimes referred to as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Through changes in the digestive system, the operation helps patients drop notable weight, so improving their health and quality of life.
The principles of gastric bypass surgery, the operation itself, its advantages, hazards, and factors to be taken into account will be discussed in this paper together with an outline of life following the surgery.
Understanding Gastric Bypass Surgery
By reducing food intake and altering the way the body absorbs nutrients, La cirugía bypass gastrointestinal está destinada a ayudar a perder peso. Those with a body mass index (BMI) over 40 or those with severe obesity-related medical problems are commonly advised this kind of surgery.Key Features of Gastric Bypass Surgery:
- Reduces stomach size significantly.
- Alters the digestive pathway, bypassing part of the small intestine.
- Results in fewer calories and nutrients being absorbed.
- Causes hormonal changes that promote a feeling of fullness.
Procedure Overview
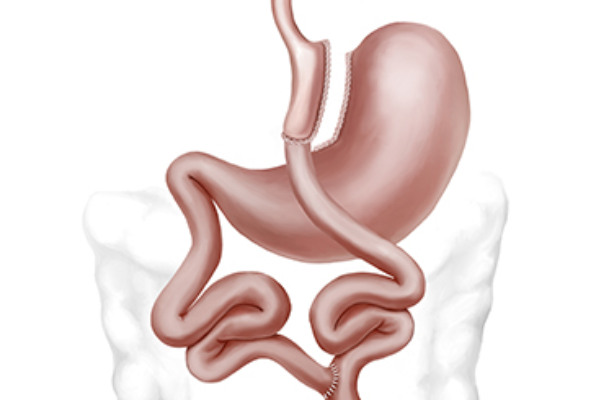
Usually, the gastric bypass operation entails making a little pouch around the size of a walnut at the top of the stomach. After that, this pouch is straight connected to the small intestine, so avoiding the first segment of the small intestine and a great portion of the stomach. The patient so eats less food and absorbs less calories.Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Anesthesia Administration: The surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety.
- Creation of a Small Stomach Pouch: A small pouch is created using surgical staples, drastically reducing the stomach’s capacity.
- Rerouting of the Digestive System: The small intestine is divided, and the lower portion is connected to the newly created pouch.
- Reconnection: The remaining part of the small intestine is attached lower down, allowing digestive juices to mix with the ingested food.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
The primary goal of gastric bypass surgery is weight loss, but the benefits extend far beyond just shedding pounds. The procedure has been shown to improve or even resolve many obesity-related health issues.
Key Benefits:
- Significant Weight Loss: Patients typically lose 60-80% of their excess body weight within 12-18 months.
- Improvement in Type 2 Diabetes: Many patients experience remission of type 2 diabetes post-surgery.
- Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Lower blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and risk of heart conditions.
- Relief from Sleep Apnea: Patients often find relief from obstructive sleep apnea.
- Better Mobility and Quality of Life: With reduced weight comes increased mobility, better self-esteem, and enhanced overall well-being.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, gastric bypass surgery comes with its share of risks. It’s essential for individuals to be aware of potential complications and prepare accordingly.
Common Risks Include:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to altered digestion, absorption of essential vitamins and minerals like calcium, iron, and vitamin B12 can be impaired.
- Dumping Syndrome: Eating certain foods too quickly can cause nausea, diarrhea, and discomfort.
- Surgical Complications: Risk of infection, bleeding, or reaction to anesthesia.
- Hernia Development: There is a risk of developing an internal hernia after the surgery.
Post-Surgery Lifestyle Changes
Gastric bypass surgery is not a quick fix; it requires a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes. A successful outcome depends on maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adhering to post-surgery guidelines.
Key Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Dietary Modifications: Focus on protein-rich foods, avoid high-fat and sugary items, and eat small portions slowly.
- Nutritional Supplements: Regular intake of multivitamins, calcium, and iron supplements is crucial.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated by drinking at least 64 ounces of water daily.
- Exercise Routine: Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
- Regular Follow-ups: Attend scheduled follow-ups to monitor weight loss and nutritional status.
Who is a Candidate for Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass surgery is not for everyone. Individuals considering this procedure must meet specific criteria and undergo a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals.
Eligibility Criteria:
- A BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions.
- Documented evidence of previous weight loss attempts through diet and exercise.
- Commitment to long-term lifestyle changes and follow-up care.
- Absence of contraindications, such as untreated mental health disorders or substance abuse.
Life After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Patients who undergo gastric bypass surgery often experience dramatic changes in their bodies and lifestyles. While the weight loss results are significant, adapting to the new dietary and exercise habits can be challenging.
Typical Changes and Adjustments:
- Emotional Changes: Weight loss may lead to unexpected emotions, requiring psychological support.
- Loose Skin: Rapid weight loss can cause excess skin, which may require corrective surgery.
- Body Image: Patients may struggle to adjust to their new body shape.
- Social and Dining Adjustments: Eating out and social events may require additional planning and dietary considerations.
Conclusion
For those suffering with extreme obesity and concomitant medical problems, gastric bypass surgery is a potent weapon. Although the operation offers enormous advantages, it also calls for a lifetime dedication to good living and medical follow-up. Anyone thinking about this road to a better life must first understand the process, risks, advantages, and lifestyle adjustments.